Coronary Heart Disease
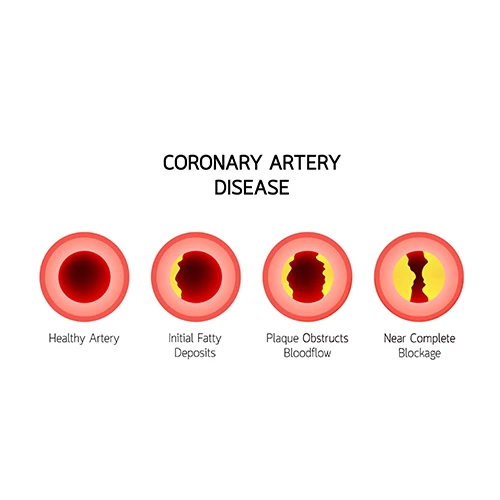
CORONOARY ARTERY DISEASE
Coronary heart disease, also known as coronary artery disease, occurs when the coronary arteries supplying blood, oxygen, and nutrients to the heart muscle become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup (atherosclerosis). This restricts blood flow, leading to symptoms like chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, or even a heart attack.
Risk factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle. CHD is a leading cause of death worldwide but can often be prevented or managed with lifestyle changes, medications, and, in some cases, surgical interventions like angioplasty or bypass surgery. Early detection and care are crucial for better outcomes.
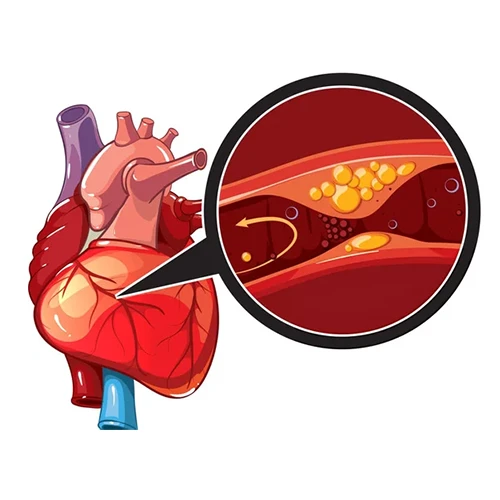
MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION (HEART ATTACK)
A myocardial infarction, commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked, usually by a blood clot or plaque rupture in a coronary artery. This interruption in blood supply prevents oxygen from reaching the heart muscle, causing tissue damage or death.
Symptoms often include chest pain or discomfort (which may radiate to the arms, neck, jaw, or back), shortness of breath, nausea, cold sweats, and fatigue.
